到目前为止,我们一直假设为了构建 Gradio 演示,你需要输入和输出。 但机器学习演示并非总是如此:例如,无条件图像生成模型不接受任何输入,而是生成图像作为输出。
So far, we've always assumed that in order to build an Gradio demo, you need both inputs and outputs. But this isn't always the case for machine learning demos: for example, unconditional image generation models don't take any input but produce an image as the output.
事实证明, gradio.Interface 类实际上可以处理 4 种不同的演示:
It turns out that the gradio.Interface class can actually handle 4 different kinds of demos:
标准演示:具有独立的输入和输出(例如图像分类器或语音到文本模型)
Standard demos: which have both separate inputs and outputs (e.g. an image classifier or speech-to-text model)
仅输出演示:不接受任何输入但产生输出(例如无条件图像生成模型)
Output-only demos: which don't take any input but produce on output (e.g. an unconditional image generation model)
仅输入演示:不产生任何输出但确实接受某种输入(例如,将图像保存到持久外部数据库的演示)
Input-only demos: which don't produce any output but do take in some sort of input (e.g. a demo that saves images that you upload to a persistent external database)
Unified demos :既有输入组件也有输出组件,但输入输出组件是一样的。 这意味着产生的输出会覆盖输入(例如文本自动完成模型)
Unified demos: which have both input and output components, but the input and output components are the same. This means that the output produced overrides the input (e.g. a text autocomplete model)
根据演示的类型,用户界面 (UI) 看起来略有不同:
Depending on the kind of demo, the user interface (UI) looks slightly different:
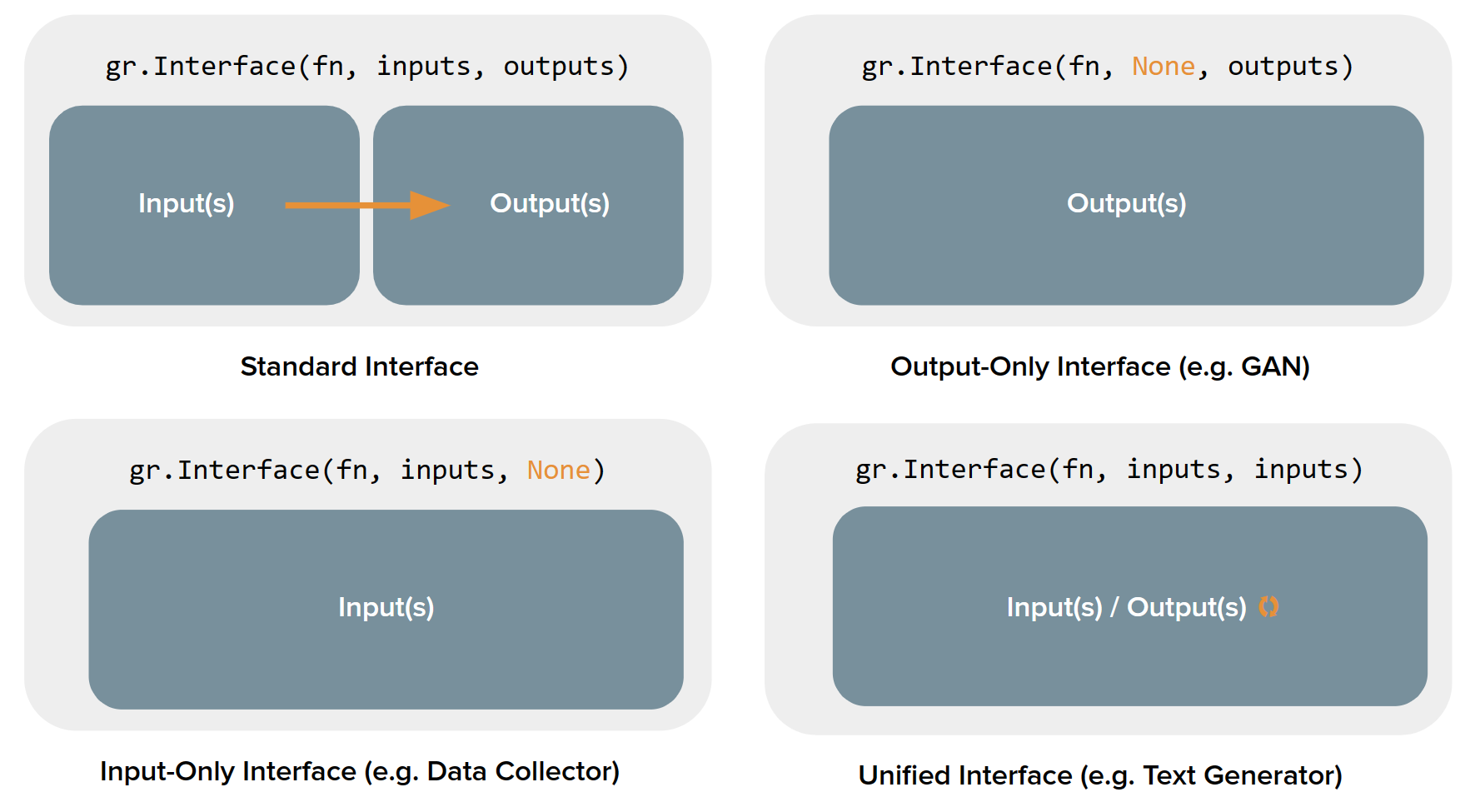
让我们看看如何使用 Interface 类构建各种演示以及示例:
Let's see how to build each kind of demo using the Interface class, along with examples:
要创建同时具有输入和输出组件的演示,你只需在 Interface() 中设置 inputs 和 outputs 参数的值。 这是一个简单图像过滤器的示例演示:
To create a demo that has both the input and the output components, you simply need to set the values of the inputs and outputs parameter in Interface(). Here's an example demo of a simple image filter:
import numpy as np
import gradio as gr
def sepia(input_img):
sepia_filter = np.array([
[0.393, 0.769, 0.189],
[0.349, 0.686, 0.168],
[0.272, 0.534, 0.131]
])
sepia_img = input_img.dot(sepia_filter.T)
sepia_img /= sepia_img.max()
return sepia_img
demo = gr.Interface(sepia, gr.Image(shape=(200, 200)), "image")
demo.launch()
只包含输出的演示怎么样? 为了构建这样的演示,你只需将 Interface() 中的 inputs 参数的值设置为 None 。 这是模拟图像生成模型的示例演示:
What about demos that only contain outputs? In order to build such a demo, you simply set the value of the inputs parameter in Interface() to None. Here's an example demo of a mock image generation model:
import time
import gradio as gr
def fake_gan():
time.sleep(1)
images = [
"https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1507003211169-0a1dd7228f2d?ixlib=rb-1.2.1&ixid=MnwxMjA3fDB8MHxwaG90by1wYWdlfHx8fGVufDB8fHx8&auto=format&fit=crop&w=387&q=80",
"https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1554151228-14d9def656e4?ixlib=rb-1.2.1&ixid=MnwxMjA3fDB8MHxwaG90by1wYWdlfHx8fGVufDB8fHx8&auto=format&fit=crop&w=386&q=80",
"https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1542909168-82c3e7fdca5c?ixlib=rb-1.2.1&ixid=MnwxMjA3fDB8MHxzZWFyY2h8MXx8aHVtYW4lMjBmYWNlfGVufDB8fDB8fA%3D%3D&w=1000&q=80",
]
return images
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=fake_gan,
inputs=None,
outputs=gr.Gallery(label="Generated Images").style(grid=[2]),
title="FD-GAN",
description="This is a fake demo of a GAN. In reality, the images are randomly chosen from Unsplash.",
)
demo.launch()
同样,要创建仅包含输入的演示,请将 Interface() 中的 outputs 参数值设置为 None 。 这是一个将任何上传的图像保存到磁盘的示例演示:
Similarly, to create a demo that only contains inputs, set the value of outputs parameter in Interface() to be None. Here's an example demo that saves any uploaded image to disk:
import random
import string
import gradio as gr
def save_image_random_name(image):
random_string = ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_letters, k=20)) + '.png'
image.save(random_string)
print(f"Saved image to {random_string}!")
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=save_image_random_name,
inputs=gr.Image(type="pil"),
outputs=None,
)
demo.launch()具有单个组件作为输入和输出的演示。 它可以简单地通过将 inputs 和 outputs 参数的值设置为同一组件来创建。 这是文本生成模型的示例演示:
A demo that has a single component as both the input and the output. It can simply be created by setting the values of the inputs and outputs parameter as the same component. Here's an example demo of a text generation model:
import gradio as gr
from transformers import pipeline
generator = pipeline('text-generation', model = 'gpt2')
def generate_text(text_prompt):
response = generator(text_prompt, max_length = 30, num_return_sequences=5)
return response[0]['generated_text']
textbox = gr.Textbox()
demo = gr.Interface(generate_text, textbox, textbox)
demo.launch()