标签:队列,性能
假设你的 Gradio 演示在社交媒体上传播开来——你有很多用户同时试用它,并且你希望为你的用户提供尽可能好的体验,或者换句话说,尽量减少每个用户使用的时间在队列中等待查看他们的预测。
Let's say that your Gradio demo goes viral on social media -- you have lots of users trying it out simultaneously, and you want to provide your users with the best possible experience or, in other words, minimize the amount of time that each user has to wait in the queue to see their prediction.
如何配置 Gradio 演示以处理最多的流量? 在本指南中,我们深入研究了 Gradio 的 .queue() 方法的一些参数以及一些其他相关配置,并讨论了如何以允许你以最小延迟同时为大量用户提供服务的方式设置这些参数。
How can you configure your Gradio demo to handle the most traffic? In this Guide, we dive into some of the parameters of Gradio's .queue() method as well as some other related configurations, and discuss how to set these parameters in a way that allows you to serve lots of users simultaneously with minimal latency.
这是一份高级指南,因此请确保你已经了解 Gradio 的基础知识,例如如何创建和启动 Gradio 界面。 无论你是在Hugging Face Spaces上还是在自己的服务器上托管演示,本指南中的大部分信息都是相关的。
This is an advanced guide, so make sure you know the basics of Gradio already, such as how to create and launch a Gradio Interface. Most of the information in this Guide is relevant whether you are hosting your demo on Hugging Face Spaces or on your own server.
默认情况下,Gradio 演示不使用队列,而是通过 POST 请求向运行 Gradio 服务器和 Python 代码的服务器发送预测请求。 然而,常规的 POST 请求有两个很大的限制:
By default, a Gradio demo does not use queueing and instead sends prediction requests via a POST request to the server where your Gradio server and Python code are running. However, regular POST requests have two big limitations:
(1) 它们超时——如果在短时间(例如 1 分钟)后没有收到对 POST 请求的响应,大多数浏览器会引发超时错误。 如果你的推理函数运行时间超过 1 分钟,或者如果许多人同时试用你的演示,从而导致延迟增加,这可能会成为一个问题。
(1) They time out -- most browsers raise a timeout error if they do not get a response to a POST request after a short period of time (e.g. 1 min). This can be a problem if your inference function takes longer than 1 minute to run or if many people are trying out your demo at the same time, resulting in increased latency.
(2) 它们不允许在 Gradio demo 和 Gradio 服务器之间进行双向通信。 这意味着,例如,你无法获得预测完成所需时间的实时 ETA。
(2) They do not allow bi-directional communication between the Gradio demo and the Gradio server. This means, for example, that you cannot get a real-time ETA of how long your prediction will take to complete.
为了解决这些限制,任何 Gradio 应用程序都可以转换为使用websockets ,只需在启动界面或块之前添加 .queue() 即可。 这是一个例子:
To address these limitations, any Gradio app can be converted to use websockets instead, simply by adding .queue() before launching an Interface or a Blocks. Here's an example:
app = gr.Interface(lambda x:x, "image", "image")
app.queue() # <-- Sets up a queue with default parameters
app.launch()
在上面的演示 app 中,预测现在将通过 websocket 发送。 与 POST 请求不同,websockets 不会超时并且它们允许双向流量。 在 Gradio 服务器上,设置了一个队列,它将每个请求添加到一个列表中。 当一个 worker 空闲时,第一个可用的请求被传递给 worker 进行推理。 当推理完成时,队列通过 websocket 将预测发送回调用该预测的特定 Gradio 用户。
In the demo app above, predictions will now be sent over a websocket instead.
Unlike POST requests, websockets do not timeout and they allow bidirectional traffic. On the Gradio server, a queue is set up, which adds each request that comes to a list. When a worker is free, the first available request is passed into the worker for inference. When the inference is complete, the queue sends the prediction back through the websocket to the particular Gradio user who called that prediction.
注意:如果你在Hugging Face Spaces上托管 Gradio 应用程序,则默认情况下已启用该队列。 你仍然可以手动调用 .queue() 方法以配置下面描述的队列参数。
Note: If you host your Gradio app on Hugging Face Spaces, the queue is already enabled by default. You can still call the .queue() method manually in order to configure the queue parameters described below.
有几个参数可用于配置队列并帮助减少延迟。 让我们一一了解它们。
There are several parameters that can be used to configure the queue and help reduce latency. Let's go through them one-by-one.
concurrency_count 参数concurrency_count parameter我们将探索的第一个参数是 queue() 的 concurrency_count 参数。 此参数用于设置 Gradio 服务器中将并行处理你的请求的工作线程数。 默认情况下,此参数设置为 1 ,但增加此参数可以线性增加服务器处理请求的能力。
The first parameter we will explore is the concurrency_count parameter of queue(). This parameter is used to set the number of worker threads in the Gradio server that will be processing your requests in parallel. By default, this parameter is set to 1 but increasing this can linearly multiply the capacity of your server to handle requests.
那么为什么不将此参数设置得更高呢? 请记住,由于请求是并行处理的,因此每个请求都会消耗内存来存储数据和权重以进行处理。 这意味着如果将 concurrency_count 增加得太高,你可能会遇到内存不足的错误。 如果 concurrency_count 由于在不同工作线程之间切换的成本过高,你也可能开始获得递减的收益。
So why not set this parameter much higher? Keep in mind that since requests are processed in parallel, each request will consume memory to store the data and weights for processing. This means that you might get out-of-memory errors if you increase the concurrency_count too high. You may also start to get diminishing returns if the concurrency_count is too high because of costs of switching between different worker threads.
建议:在你继续看到性能提升或达到计算机内存限制之前,尽可能高地增加 concurrency_count 参数。 你可以在此处阅读有关 Hugging Face Spaces 机器规格的信息。
Recommendation: Increase the concurrency_count parameter as high as you can while you continue to see performance gains or until you hit memory limits on your machine. You can read about Hugging Face Spaces machine specs here.
注意:还有第二个参数控制 Gradio 可以生成的线程总数,无论是否启用队列。 这是 launch() 方法中的 max_threads 参数。 当你增加 queue() 中的 concurrency_count 参数时,它也会自动增加。 但是,在某些情况下,你可能希望手动增加它,例如,如果未启用排队。
Note: there is a second parameter which controls the total number of threads that Gradio can generate, whether or not queuing is enabled. This is the max_threads parameter in the launch() method. When you increase the concurrency_count parameter in queue(), this is automatically increased as well. However, in some cases, you may want to manually increase this, e.g. if queuing is not enabled.
max_size 参数max_size parameter一个更直截了当的减少等待时间的方法就是从一开始就防止太多人加入队列。 你可以使用 queue() 的 max_size 参数设置队列处理的最大请求数。 如果请求在队列已经达到最大大小时到达,则不允许加入队列,相反,用户将收到一条错误消息,指出队列已满并重试。 默认情况下, max_size=None ,这意味着可以加入队列的用户数量没有限制。
A more blunt way to reduce the wait times is simply to prevent too many people from joining the queue in the first place. You can set the maximum number of requests that the queue processes using the max_size parameter of queue(). If a request arrives when the queue is already of the maximum size, it will not be allowed to join the queue and instead, the user will receive an error saying that the queue is full and to try again. By default, max_size=None, meaning that there is no limit to the number of users that can join the queue.
矛盾的是,设置 max_size 通常可以改善用户体验,因为它可以防止用户被非常长的队列等待时间劝阻。 对你的演示更感兴趣和投入更多的用户将继续尝试加入队列,并且能够更快地获得结果。
Paradoxically, setting a max_size can often improve user experience because it prevents users from being dissuaded by very long queue wait times. Users who are more interested and invested in your demo will keep trying to join the queue, and will be able to get their results faster.
建议:为了获得更好的用户体验,请根据你对用户可能愿意等待预测多长时间的预期设置合理的 max_size 。
Recommendation: For a better user experience, set a max_size that is reasonable given your expectations of how long users might be willing to wait for a prediction.
max_batch_size 参数max_batch_size parameter另一种提高 Gradio 演示并行性的方法是编写你的函数,使其可以接受成批输入。 大多数深度学习模型可以比处理单个样本更有效地处理成批样本。
Another way to increase the parallelism of your Gradio demo is to write your function so that it can accept batches of inputs. Most deep learning models can process batches of samples more efficiently than processing individual samples.
如果你编写函数来处理一批样本,Gradio 会自动将传入请求一起批处理,并将它们作为一批样本传递到你的函数中。 你需要将 batch 设置为 True (默认情况下为 False )并根据你的函数能够处理的最大样本数设置 max_batch_size (默认情况下为 4 )。 这两个参数可以传递到 gr.Interface() 或块中的事件,例如 .click() 。
If you write your function to process a batch of samples, Gradio will automatically batch incoming requests together and pass them into your function as a batch of samples. You need to set batch to True (by default it is False) and set a max_batch_size (by default it is 4) based on the maximum number of samples your function is able to handle. These two parameters can be passed into gr.Interface() or to an event in Blocks such as .click().
虽然设置批次在概念上类似于让工作人员并行处理请求,但它通常比为深度学习模型设置 concurrency_count更快。 缺点是你可能需要稍微调整你的功能以接受批量样本而不是单个样本。
While setting a batch is conceptually similar to having workers process requests in parallel, it is often faster than setting the concurrency_count for deep learning models. The downside is that you might need to adapt your function a little bit to accept batches of samples instead of individual samples.
下面是一个不接受批量输入的函数示例——它一次处理一个输入:
Here's an example of a function that does not accept a batch of inputs -- it processes a single input at a time:
import time
def trim_words(word, length):
return w[:int(length)]
这是重写的相同函数以接收一批样本:
Here's the same function rewritten to take in a batch of samples:
import time
def trim_words(words, lengths):
trimmed_words = []
for w, l in zip(words, lengths):
trimmed_words.append(w[:int(l)])
return [trimmed_words]
第二个函数可以与 batch=True 和适当的 max_batch_size 参数一起使用。
The second function can be used with batch=True and an appropriate max_batch_size parameter.
建议:如果可能,编写你的函数以接受样本批次,然后根据你机器的内存限制将 batch 设置为 True 和 max_batch_size 尽可能高。 如果你将 max_batch_size 设置得尽可能高,你很可能需要将 concurrency_count 设置回 1 ,因为你将不再有内存让多个 worker 并行运行。
Recommendation: If possible, write your function to accept batches of samples, and then set batch to True and the max_batch_size as high as possible based on your machine's memory limits. If you set max_batch_size as high as possible, you will most likely need to set concurrency_count back to 1 since you will no longer have the memory to have multiple workers running in parallel.
api_open 参数api_open parameter创建 Gradio 演示时,你可能希望限制所有流量通过用户界面发生,而不是通过为 Gradio 演示自动创建的编程 API 。 这很重要,因为当人们通过编程 API 发出请求时,他们可能会绕过在队列中等待的用户并降低这些用户的体验。
When creating a Gradio demo, you may want to restrict all traffic to happen through the user interface as opposed to the programmatic API that is automatically created for your Gradio demo. This is important because when people make requests through the programmatic API, they can potentially bypass users who are waiting in the queue and degrade the experience of these users.
建议:在演示中将 queue() 中的 api_open 参数设置为 False 以防止编程请求。
Recommendation: set the api_open parameter in queue() to False in your demo to prevent programmatic requests.
如果你已完成上述所有操作,但你的演示仍然不够快,你可以升级模型运行的硬件。 将模型从在 CPU 上运行更改为在 GPU 上运行通常会使深度学习模型的推理时间增加 10-50 倍。
If you have done everything above, and your demo is still not fast enough, you can upgrade the hardware that your model is running on. Changing the model from running on CPUs to running on GPUs will usually provide a 10x-50x increase in inference time for deep learning models.
在 Hugging Face Spaces 上升级硬件特别简单。 只需单击空间中的“设置”选项卡,然后选择你喜欢的空间硬件。
It is particularly straightforward to upgrade your Hardware on Hugging Face Spaces. Simply click on the "Settings" tab in your Space and choose the Space Hardware you'd like.
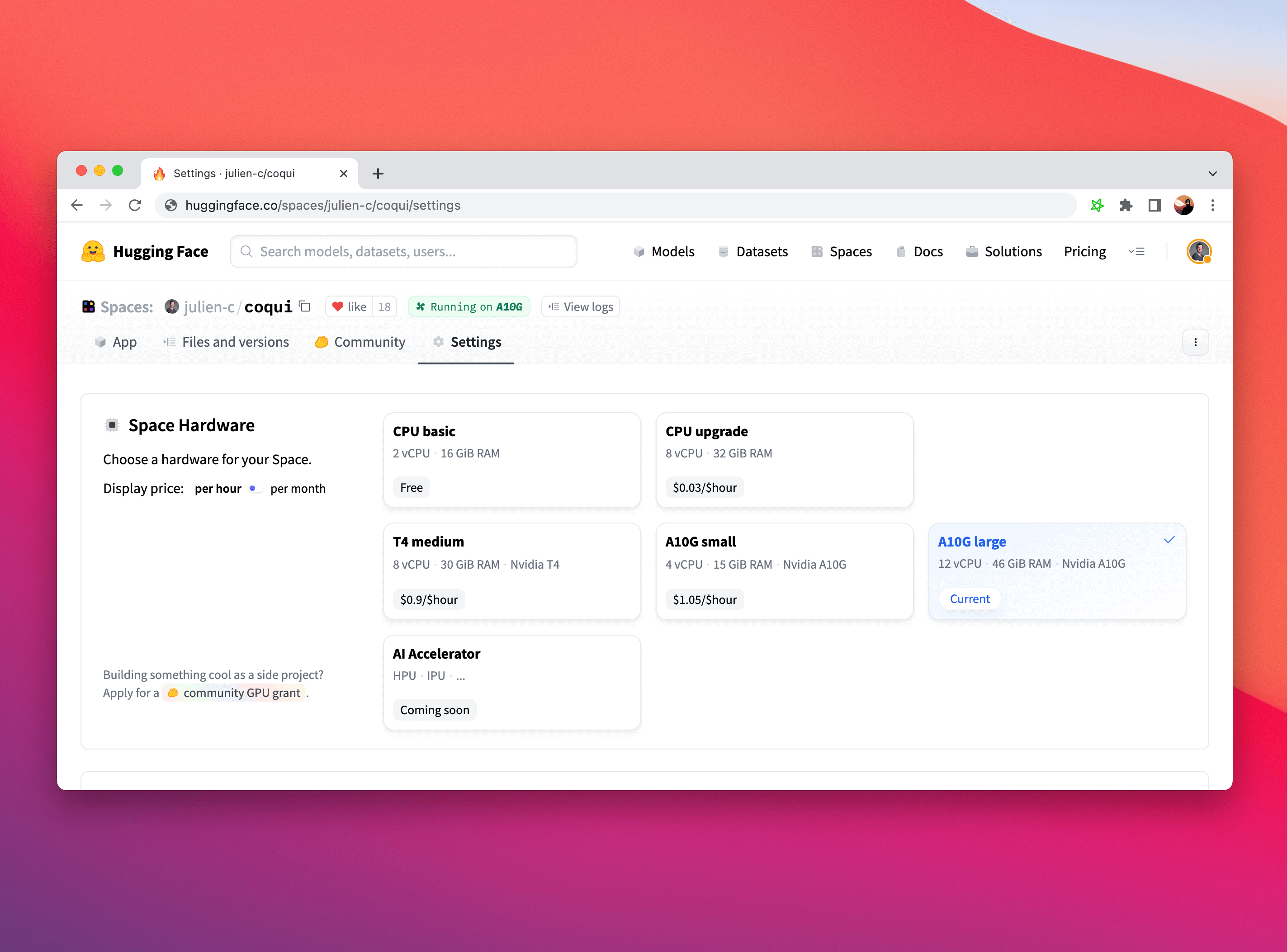
虽然你可能需要调整部分机器学习推理代码以在 GPU 上运行(如果你使用 PyTorch,这里有一个方便的指南),但 Gradio 完全不知道硬件的选择,如果你将它与 CPU 一起使用,它将完全正常工作、GPU、TPU 或任何其他硬件!
While you might need to adapt portions of your machine learning inference code to run on a GPU (here's a handy guide if you are using PyTorch), Gradio is completely agnostic to the choice of hardware and will work completely fine if you use it with CPUs, GPUs, TPUs, or any other hardware!
注意:你的 GPU 内存不同于 CPU 内存,因此如果你升级硬件,你可能需要调整上述 concurrency_count 参数的值。
Note: your GPU memory is different than your CPU memory, so if you upgrade your hardware,
you might need to adjust the value of the concurrency_count parameter described above.
恭喜! 你知道如何设置 Gradio 演示以获得最佳性能。 祝你的下一个病毒演示好运!
Congratulations! You know how to set up a Gradio demo for maximum performance. Good luck on your next viral demo!